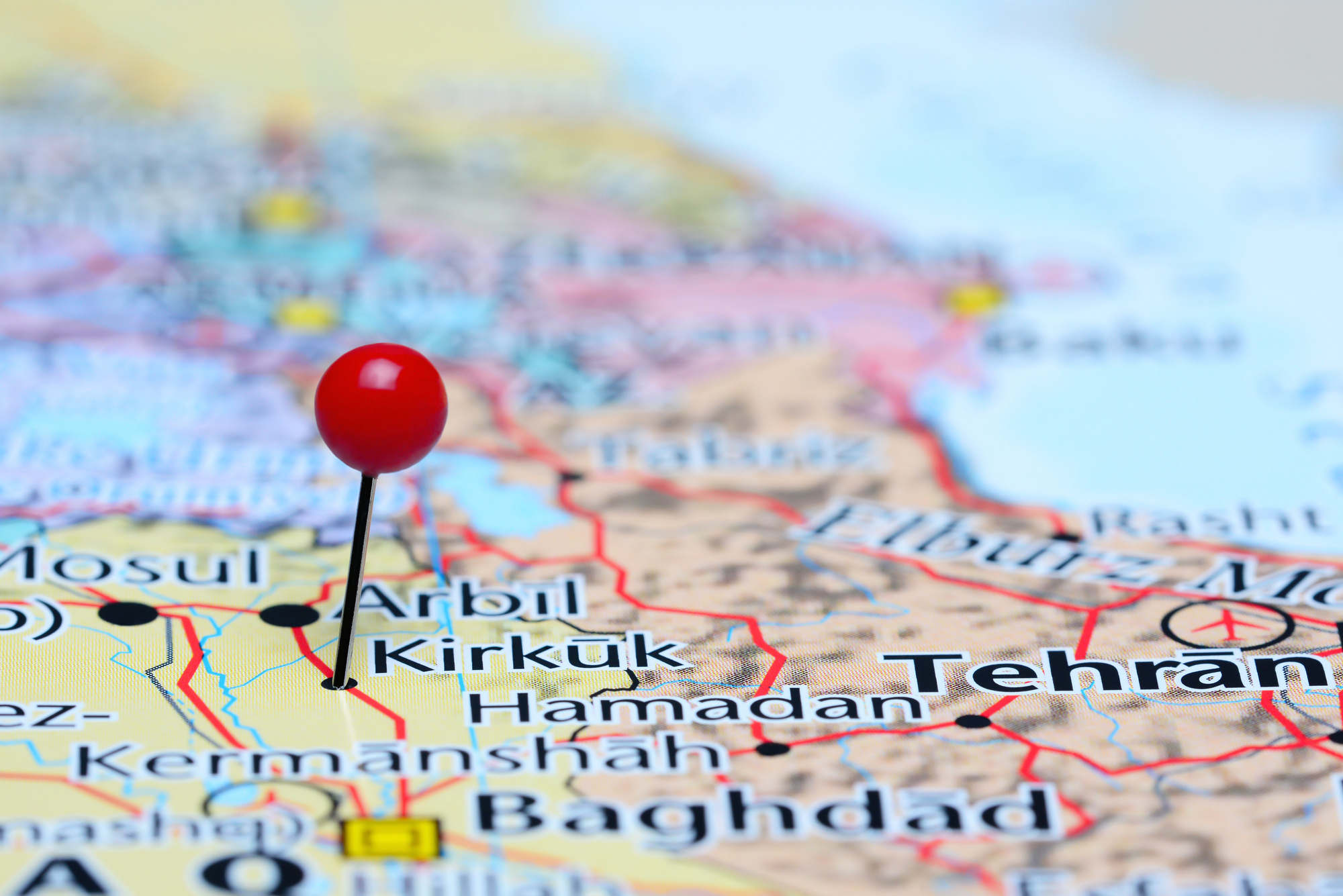
Kirkuk Crude Oil of Iraq: Its History, Price, and Production
Kirkuk crude oil is one of the most sought-after types of petroleum because it is high quality and relatively inexpensive. Located in Iraq, Kirkuk crude oil is an essential source for many countries worldwide.
It has been used as a significant export of Iraq since 1933. The production of Kirkuk crude oil has experienced numerous changes over the years, with periods of increased output and others with production stops due to conflict.
Geology of Kirkuk
Kirkuk, Iraq, is an ancient city inhabited since the beginning of civilization, and its geology has played a prominent role in shaping the region’s history.
Located in Northern Iraq, Kirkuk sits atop a wealth of natural resources, particularly crude oil. This natural resource has been mined since ancient times and is a significant factor in the regional economy.
Two main geological features dominate Kirkuk’s geology: sedimentary rocks and igneous intrusions. The sedimentary rocks are responsible for the vast amounts of crude oil found beneath the surface.
At the same time, igneous intrusions have caused active volcanoes that have erupted over time, adding further complexity to this ancient landscape.
These geological forces have shaped both terrain and climate – creating pockets of arid lands interspersed with lush greenery fed by rivers flowing through canyons carved centuries ago.
History of Oil Exploration and Production
The city of Kirkuk, located in northern Iraq, has a long and rich history when it comes to oil production. Kirkuk’s oil reserves have been mined for centuries, dating back to the Ottoman Empire in the early 19th century.
By the end of World War I, British forces had taken control of what would become known as Iraq; with them came modern oil drilling technology and an influx of foreign investment in Kirkuk’s oil industry. Fast forward to today, and Kirkuk is said to possess some of the largest oil fields in the world.
Since 2003, much has changed for Kirkuk’s economy due to its volatile political climate; however, oil remains a significant source of income for both foreign investors and locals alike.
Furthermore, in recent years production levels have gone up significantly due to new technological advancements implemented by international organizations such as OPEC.
Impact on Iraq’s Economy
Kirkuk is a major contributor to Iraq’s economy thanks to its oil production and export capabilities. It holds some of Iraq’s largest crude oil reserves, estimated at around 9 billion barrels.
This makes the city an invaluable asset for the nation’s economic growth.
The Kirkuk province alone produces nearly 500,000 barrels of crude oil per day, and this number could increase if more investments were made in the area.
Moreover, with current production levels, Kirkuk provides an essential source of revenue for Iraq through taxes on exports and income from foreign investments in the industry – especially considering that Iraq largely depends on crude oil exports for economic stability.
The city has experienced both prosperity and strife throughout its history, but it continues to be a key player in the Iraqi economy with immense potential for further growth.
Conflict & Politics Surrounding Kirkuk Oil
The oil-rich city of Kirkuk in Iraq has long been a source of political and military contention. As one of the essential sources of crude oil in the world, its control has been fought over by foreign countries and regional powers for decades.
However, the latest dispute began when Islamic State militants seized the city in 2014. This triggered an armed conflict between Kurdish forces, backed by the United States, and Iraqi government troops, with both sides vying for control of this strategic resource.
Since then, various parties have claimed Kirkuk’s massive oil reserves, including Turkey and Iran, which view it as critical to their economic growth. In response to these geopolitical pressures, Iraq’s Prime Minister Haider al-Abadi declared federal authority over Kirkuk’s resources earlier this year to settle ownership rights.
Kirkuk–Ceyhan Oil Pipeline
The Kirkuk Ceyhan Oil Pipeline stretches from Iraq to Turkey and is a vital artery for the global oil markets. Built-in the late 1990s and running along an 800 km route from Kirkuk in northern Iraq to the Turkish port city of Ceyhan on the Mediterranean Sea, this pipeline transports crude oil to international buyers.
This strategic export route provided crucial support for Iraq’s economy and has become a significant source of income since its construction.
The first Iraqi exports through the pipeline began in 2000 and have been growing, with over two billion barrels of crude being transported yearly. This oil is exported to European countries such as Italy and France and other nations worldwide, including China, India and Japan.
Price of Kirkuk Crude Oil
The price of Kirkuk, an Iraqi crude is assessed FOB Ceyhan, and is calculated by applying differentials of Kirkuk to the current Dated Brent price. Where there are no trades, the price assessment is left unchanged.
This assessment reflects the shipment of Iraqi crude oil from Kirkuk to Ceyhan in Turkey, with a typical charge size of 600,000 barrels, but cargoes up to 1 million barrels can be used for evaluation.
The normal freight price period is 3-5 days after bill of lading. The analysis covers only Iraqi crude shipments from Kirkuk and does not include KBT shipments loaded from Bottas station in Ceyhan.
Kirkuk vs Med Dated Brent Strip is also assessed and published by price reporting agencies.
Owners and Operators
Kirkuk, Iraq, is the centre of much oil production and commercial activity. The state-owned Iraqi State Oil Marketing Organization (SOMO) has been a major player in this activity for several decades. But other foreign companies have recently entered the market.
These international firms have invested heavily in exploring and producing oil from Kirkuk’s vast reserves. They use cutting-edge technology to maximize their operations’ efficiency, safety and environmental protection.
ExxonMobil and BP have built new facilities for refining, storing and transporting crude oil from Kirkuk’s fields, helping drive economic progress throughout Iraq.
In addition to providing jobs for local citizens, these companies are also setting high-performance standards regarding corporate responsibility and sustainability practices.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Kirkuk Crude Oil is a highly sought-after commodity due to its premium quality and high production rate. For over 70 years, oil has been at the centre of international politics, economic growth, and stability in Iraq and the Middle East.
It remains an essential resource for the region and an important source of revenue for the Iraqi government. Therefore, Kirkuk Crude Oil is a valuable asset that will continue to provide many benefits for years.




0 Comments